Understanding Goal Management and Its Importance for SME Teams
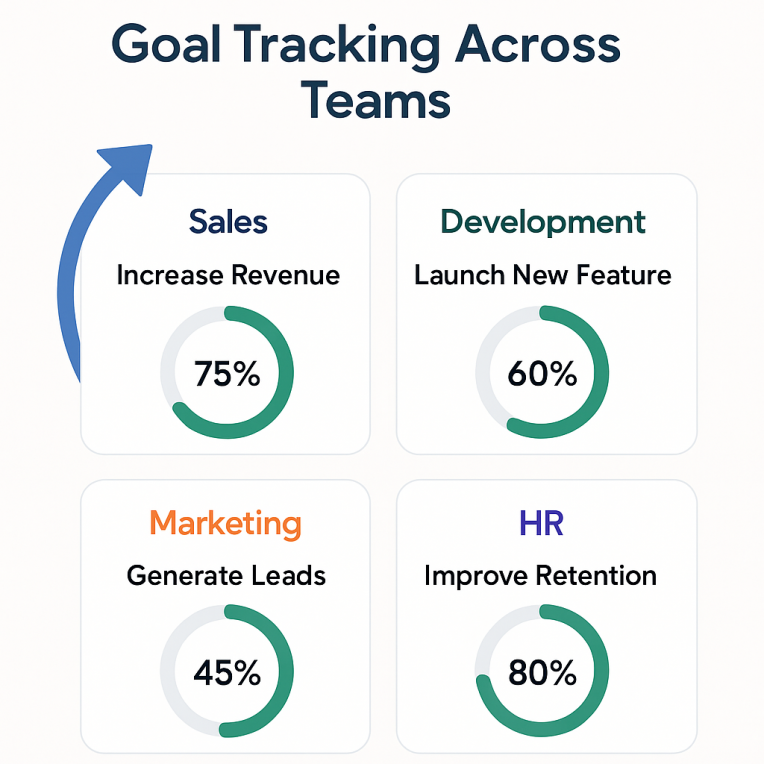
Goal management is the practice of defining, tracking, and achieving organizational goals across teams. It provides clear direction and focus for everyone, aligning individual work with company objectives. In small and medium enterprises, this alignment is crucial: setting clear, measurable goals guides teams to apply their energy effectively toward shared outcomes. Well-defined goals also motivate employees and boost engagement. Studies find that when people see how their personal goals tie to the company’s objectives, they are significantly more productive and engaged. By establishing specific targets and regularly reviewing progress, SMEs can use goal management to improve planning, accountability, and performance evaluation.
- Clear Direction: Goals give teams a shared destination and milestones to aim for.
- Employee Engagement: Committed, ambitious goals motivate staff. Employees with aligned goals perform better and feel more ownership of their work.
- Performance Measurement: Defined goals create benchmarks. Tracking progress with KPIs or key results provides data for evaluating performance and making timely adjustments.
- Adaptability: In SMEs where resources are tight, goal management helps prioritize work and adapt quickly to change. It fosters a culture where everyone understands “how we’ll know we’re winning,” reducing confusion and wasted effort.
By emphasizing goal alignment across teams, SME leaders ensure that every department – whether sales, development, or HR – pulls in the same direction. This alignment not only enhances productivity but also strengthens collaboration, as everyone clearly sees how their tasks contribute to bigger-picture success.

Major Goal-Setting Frameworks and When to Use Them
SME teams employ different goal-setting frameworks depending on their needs. The right strategy will align with your team’s workflow and objectives. Below are four popular approaches used by high-performing companies:
OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
What are OKRs? OKRs are a goal-setting framework of qualitative objectives and quantitative key results. An Objective answers “Where do we want to go?” and is supported by 3–5 Key Results that answer “How will we measure progress?”. OKRs were popularized by Intel and spread through Silicon Valley giants like Google. They are ambitious and collaborative, designed to create alignment and engagement around measurable outcomes.
- Usage in High-Performers: Tech and product teams use OKRs quarterly to drive innovation. Google (with 100,000+ employees) still uses OKRs to connect individual work to company strategy. Others like LinkedIn and Airbnb set company-wide OKRs, then cascade them to teams.
- Best for: Fast-moving or cross-functional teams (e.g. engineering, marketing, R&D) that need agility. OKRs fit environments where stretch targets push teams beyond “business as usual.” They work well in startups and growing SMEs aiming to scale and stay focused on key priorities.
- Why It Works: OKRs make strategy transparent. Teams see how each member’s efforts contribute to big goals, increasing engagement. They shift the mindset from “busy work” to “moving the needle”. Regular OKR check-ins (often weekly or monthly) help spot blockers and adapt quickly.
SMART Goals
What are SMART Goals? SMART is an acronym for goals that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This widely-used framework ensures objectives are clear and realistic. For example, a SMART goal might be “Increase new customer sign-ups by 20% in Q4.”
- Usage in High-Performers: Most companies across functions use SMART criteria. Sales teams set SMART revenue targets; HR sets SMART recruitment or retention goals. It’s taught in business schools and common in annual planning.
- Best for: Contexts where clarity and feasibility matter. SMART is ideal for well-defined projects, individual performance plans, and operational goals in both small teams and large organizations. It’s useful in stable environments where overly ambitious stretch goals might demotivate.
- Why It Works: By forcing specificity and deadlines, SMART goals prevent vague objectives. They simplify tracking and accountability. (Notably, Google famously opts for “stretch” goals instead of strictly “achievable,” believing ambitious targets can spur performance.)
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators)
What are KPIs? KPIs are quantitative metrics that track how effectively a team or business is achieving its objectives. They can be financial (e.g. revenue, profit), customer-related (e.g. Net Promoter Score), operational (e.g. defect rate), or process-oriented (e.g. cycle time). Well-chosen KPIs provide “clear visibility into performance”.
- Usage in High-Performers: Leading firms set 5–7 KPIs per strategic goal. For example, a retail SME might track KPIs like same-store sales, conversion rate, and average order value. Manufacturers might use KPIs for on-time delivery and quality.
- Best for: Any team that needs objective measures. Sales, marketing, and customer service teams use KPIs daily. Operations teams use them for efficiency metrics. KPIs are especially valuable in businesses with repetitive processes, where performance can be quantified.
- Why It Works: By focusing on “what matters,” KPIs keep teams aligned on success metrics. They also underpin other frameworks (for instance, Balanced Scorecards use KPIs in different perspectives). Regular KPI reviews inform decisions and highlight areas needing attention.
Balanced Scorecards
What is a Balanced Scorecard? The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic performance management framework that translates a company’s vision into a balanced set of measures. It adds non-financial views (customer, internal process, learning/growth) to traditional financial metrics. The four perspectives ensure an organization doesn’t focus on profits alone but also on customer satisfaction, operational excellence, and employee development.
- Usage in High-Performers: Many established companies (particularly large enterprises) use Balanced Scorecards during strategic planning. Founders Robert Kaplan and David Norton introduced it at companies wanting to “measure what matters beyond finances”. It’s common in long-range planning and board-level reviews.
- Best for: Organizations needing a holistic view. Balanced Scorecards suit firms with multiple departments, helping align departmental goals with corporate strategy. For example, an SME might have a mini-scorecard with KPIs for profit, customer retention, process efficiency, and employee training.
- Why It Works: It forces trade-offs and balanced improvements. High-performers use it to ensure, say, that improving finance KPIs doesn’t hurt customer satisfaction or innovation. By cascading a Balanced Scorecard through departments, every team sees how their goals fit the big picture.
Each approach has its strengths. OKRs excel in dynamic, collaborative environments. SMART goals shine when clarity and simplicity are needed. KPIs provide the hard data to track success. Balanced Scorecards tie everything together at the strategic level. The best goal-setting strategy depends on team context: for example, a software dev team may prefer OKRs for agility, while an accounting team might stick to KPIs and SMART goals. By understanding these frameworks, SME leaders can choose the right mix for their teams.
Top Goal Management Software Platforms for Teams
Effective goal management often relies on software tools. Here are some leading platforms used by SMEs and larger firms alike:
- Asana (Work Management + Goals): Best known for project and task management, Asana also offers a robust Goals feature. Teams can define objectives or OKRs and link them to projects and tasks. As work is done in Asana, goal progress updates automatically. Dashboards and status reports make it easy to see which goals are On Track or At Risk. Asana suits cross-functional teams that already use it for projects – now they can track goals without leaving the platform.
- Lattice (People & Performance Platform): Lattice is an integrated people management suite. In addition to performance reviews, 1:1s, and engagement surveys, it includes an OKR & Goals module. Teams can set company, team, and individual OKRs, then discuss progress in reviews and check-ins. Lattice targets HR and leadership: it’s ideal for teams that want to tie goal-setting into employee development and feedback cycles. Large teams that need continuous performance management (especially those with established HR processes) gravitate to Lattice.
- 15Five (OKRs + Continuous Feedback): 15Five emphasizes continuous performance enablement. Its OKR tools help organizations “get total alignment, crystal-clear focus, and super engaged teams”. In practice, 15Five lets teams build OKRs, then supports weekly check-ins, pulse surveys, and coaching. It’s popular with startups and growth-stage companies that want an all-in-one HR solution. Users praise 15Five for integrating goal-setting with ongoing manager-employee conversations and real-time progress tracking.
- Betterworks (Enterprise OKRs & PM): Betterworks is geared toward enterprise-grade goal management. It provides continuous performance management built around OKRs and regular check-ins. Teams can set and align company-wide OKRs, run frequent one-on-ones, gather peer feedback, and analyze progress with built-in analytics. Its focus on scalability and data-driven HR makes it a choice for larger organizations and SMEs that anticipate rapid growth. Betterworks is often used by businesses that want a structured, analytics-heavy approach to tying goals into overall workforce performance (though its complexity can exceed the needs of very small teams).
- Weekdone (OKRs for SMBs): Weekdone is designed specifically for small to mid-sized teams (“built for SMBs”). It combines OKRs with weekly planning and reporting. Teams set annual or quarterly OKRs and break them down into weekly projects and tasks. Weekly check-ins on progress (Plans, Progress, Problems) keep everyone aligned. Users like Weekdone for its simplicity: it provides visual OKR hierarchies, status colors, and basic feedback/kudos. It’s a popular OKR tool for SMEs because it’s affordable, easy to use, and focuses on the core goal-setting disciplines (alignment, weekly tracking, and simple dashboard reporting).
Each of these tools addresses goal tracking in different ways. Asana ties goals to project work; Lattice and 15Five integrate goals into HR workflows; Betterworks offers enterprise-grade OKR programs; and Weekdone gives a lightweight OKR dashboard for smaller teams.
| Feature / Capability | Asana | Lattice | 15Five | Betterworks | Weekdone | Atwork (Unified Work OS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goal/OKR Support | Yes – goals & OKRs linked to projects | Yes – company, team & individual OKRs | Yes – company & individual OKRs | Yes – enterprise OKRs & goals | Yes – company/department/team OKRs | Yes – flexible goal definitions on any integrated data |
| Task & Project Management | Robust – Kanban, Gantt, lists | No – Focus is on people data | No – Focus is on feedback | No – Focus is on goals/perf | Basic – link projects to OKRs | Full – Advanced tasks (Kanban, Gantt) |
| Built-in CRM/Client Tracking | No (requires add-on/integration) | No | No | No | No | Yes – Native CRM with pipelines |
| Performance Management (HR) | Limited (goals only) | Yes – reviews, feedback, 1:1s | Yes – check-ins, surveys | Yes – continuous PM features | Limited (OKRs + feedback) | Yes – Org chart, skill tracking, workload insights |
| Custom Data & Integrations | Many apps (Slack, Salesforce) | Integrates (Slack, etc.) | Integrates (Slack, Jira, etc.) | Integrates (OKR/HR apps) | Integrates (Jira, HubSpot, etc.) | Any data source – CSV, API, databases (goals on any metric) |
| AI/Automation Support | No (but has basic rules) | No | No | Limited | No | Yes – AI assistant for workflow automation and recommendations |
| Best For | Cross-team projects & OKRs | HR-driven performance management | Engaged teams with continuous feedback | Large organizations/enterprises | SMBs & startups | Any SME – unified goals, tasks, CRM, analytics |
Atwork’s Unified Goal Management Solution
SME leaders looking for a truly unified solution should consider Atwork. Unlike specialized tools, Atwork is a customizable Work OS that brings task management, customer management (CRM), forms, and goal tracking under one roof. This integration is Atwork’s key advantage:
- Goals Linked to Real Work: In Atwork, you can set goals on any data source – tasks, deals, support tickets, custom fields, spreadsheets or APIs. For example, a sales goal can automatically pull data from the CRM pipeline, while a support team’s goal can update from ticket resolutions. This means goal progress updates in real time as work happens, without manual data entry.
- Integrated Task & Project Context: Because Atwork’s goal module is tied to its task management, managers can prioritize the right work by linking objectives to specific projects or workflows. Team members see how their daily tasks ladder up to higher-level goals, boosting motivation and clarity.
- Built-in Analytics & Insights: Atwork delivers real-time dashboards that span all functions. Users gain actionable insights on productivity and trends by combining task data with goals and customer info. For instance, leaders can spot a lagging sales goal and drill down to see which sales rep or market is underperforming – all from one dashboard. By leveraging AI, Atwork even automates routine updates and highlights potential blockers.
- Increased Alignment & Productivity: Having one platform for goals, tasks, and customers eliminates silos. Teams no longer switch between separate tools for projects and goal tracking. This unified approach makes it easier to keep everyone on the same page. In fact, when companies align goals across all levels, employees work more efficiently and collaboratively.
In short, Atwork extends goal management far beyond OKRs or KPI spreadsheets. It creates a single source of truth: tasks, customer pipelines, and performance targets are all connected. Teams spend less time chasing status updates and more time executing. With Atwork, SME teams gain the benefits of goal-setting (direction, motivation, measurement) plus the power of integrated data and AI-driven insights.
Comparison Table: The table above highlights how Atwork’s unified platform combines the strengths of task management, CRM, and goal tracking. While tools like Asana, Lattice, 15Five, Betterworks, and Weekdone each excel in their niches (project planning, HR, OKRs, etc.), Atwork uniquely ties them all together. This all-in-one design saves time and boosts alignment – it’s essentially “goal management software for teams” taken to the next level, making it an ideal solution for modern SMEs seeking a comprehensive performance tracking tool.